Radical Innovation Meaning, Examples and Characteristics
Published: 17 December, 2023
Innovation

Table of Contents
Radical innovation is the main type of innovation that involves the integration of groundbreaking technology and novel business approaches, surpassing the scope of incremental innovation and disruptive innovation. While incremental steps enhance existing products or services, radical innovation brings about transformative changes in how we live or how businesses operate. Embracing radical innovation allows companies to establish themselves as pioneers in innovation, trendsetters, and influencers in the market, providing them with significant competitive advantages over less innovative counterparts.
At Digital Leadership, our specialized Innovation Consulting services centre around harnessing radical innovation to help emerging brands identify industry gaps and overlooked segments. We support businesses in seizing opportunities presented by emerging technologies. We offer Innovation Blueprint service functions as the initial step, conducting a thorough assessment of existing innovation practices and seamlessly incorporating them into the overarching business strategy.
What is Radical Innovation?
Radical innovation represents a paradigm shift, a departure from the conventional towards groundbreaking transformations. It is characterized by its profound impact, challenging existing norms and introducing novel technologies, processes, or business models. In a radical innovation, a firm targets a groundbreaking and transformative form of innovation, encapsulating a departure from incremental improvements or minor modifications.
Radical Innovation Definition
Radical innovation is a term that encapsulates a groundbreaking and transformative form of innovation. At its core, the definition of radical innovation lies in its departure from incremental improvements or minor modifications. Instead, it represents a profound shift in thinking, technology, or business models. This type of innovation introduces entirely new concepts, products, or services that challenge existing norms and redefine industries. The radical innovation meaning is characterized by its disruptive impact, creating a significant departure from the established status quo. In essence, radical innovation is not an incremental enhancement but a revolutionary leap, paving the way for novel solutions, approaches, and opportunities.
The Jobs to be done theory offers a deep understanding of the fundamental motivations behind customer choices, illuminating the “jobs” customers are trying to accomplish. This insight becomes a valuable foundation for radical innovation, guiding the development of products or services that not only meet existing needs but also redefine the customer experience.

Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Source: Helge Tennø.
For a deeper understanding of types of innovation and other approaches to innovation strategy, you can explore our book “How to Create Innovation.” It provides valuable insights and practical guidance on leveraging these canvases to drive business growth and success.
Radical Innovation Examples
Radical innovation stands as a beacon of transformative change, reshaping industries and pushing the boundaries of what was once considered possible. Examples of radical innovation serve as vivid illustrations of how certain groundbreaking inventions have not just evolved but revolutionized entire sectors. These innovations represent more than incremental advancements; they mark paradigm shifts, introducing novel technologies, business models, and ways of thinking.
From the advent of personal computers that democratized access to computing power to blockchain technology’s decentralized revolution and the introduction of electric vehicles challenging traditional transportation, these examples showcase the essence of radical innovation—where ideas transcend conventional boundaries, bringing about profound and lasting impact. Let’s embark on a journey through these exemplars of innovation, exploring the transformative power that radical thinking has had on our world.
Personal Computers:
The advent of personal computers brought about a paradigm shift in the way people and businesses engaged with technology, ushering in transformative changes across various industries. Several companies played pivotal roles in the development and popularization of personal computers, shaping the landscape of modern computing. Notable examples include:
Apple Inc.:
Apple stands as an iconic figure in the personal computer revolution. The Apple II, introduced in 1977, marked a significant milestone as one of the earliest successful mass-produced microcomputers. However, it was the release of the Macintosh in 1984, featuring a graphical user interface and a mouse, that played a crucial role in driving the widespread adoption of personal computers.
IBM:
International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) holds a central position in the history of personal computers. The introduction of the IBM Personal Computer (IBM PC) in 1981 set a standard for both business and home computing. IBM’s strategic choice of open architecture and third-party components significantly contributed to the broad acceptance of IBM-compatible PCs.
Microsoft Corporation:
Microsoft emerged as a key player in the personal computer revolution by developing the MS-DOS operating system tailored for IBM PCs. The company’s software, including the ubiquitous Windows operating system, became integral to the global success and ubiquity of personal computers.
Cloud Technology:
Cloud technology has significantly reshaped the landscape of data storage, processing, and accessibility, presenting businesses with scalable and flexible solutions. Let’s delve into the profound impact of cloud technology with real-life illustrations:
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
A frontrunner in cloud services, AWS provides an extensive range of offerings, encompassing computing power, storage solutions, and databases. Renowned entities such as Netflix, Airbnb, and Spotify rely on AWS to dynamically scale their operations, seamlessly adjusting to fluctuating demand.
Microsoft Azure:
Microsoft’s cloud platform, Azure, presents a comprehensive suite of services covering computing, analytics, storage, and networking. Esteemed organizations like Adobe and BMW have harnessed Azure to elevate their digital capabilities, integrating tools for data analytics, artificial intelligence, and more.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
Google Cloud delivers a diverse set of cloud services, spanning computing, storage, and machine learning. Companies like PayPal and Twitter have embraced GCP to fortify their infrastructure, empowering them to handle extensive transactions and efficiently process vast amounts of data.
Washing Machine:
The washing machine, a revolutionary household appliance, brought about a transformation in domestic chores by automating a once labor-intensive process, resulting in substantial time and effort savings. Let’s explore real-life examples of companies that have played pivotal roles in the development and innovation of washing machines:
Whirlpool Corporation:
A prominent multinational manufacturer of home appliances, Whirlpool has been a trailblazer in the introduction of innovative features and technologies in washing machines. Their focus extends to enhancing efficiency, promoting water conservation, and ensuring user convenience.
Samsung Electronics:
A global electronics giant, Samsung is renowned for its diverse range of appliances, including washing machines. Samsung has propelled innovation in this domain by introducing smart washing machines equipped with features such as app-based controls, AI-powered automation, and energy-efficient technologies.
LG Electronics:
Another major player in the home appliance industry, LG offers a variety of washing machines. LG has consistently been at the forefront of innovation by introducing technologies like direct drive motors and steam cleaning features, aiming to improve washing performance while concurrently reducing energy consumption.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, recognized for its initial application in cryptocurrencies, has introduced a decentralized and secure method of recording and verifying transactions. This innovative technology goes beyond the realm of digital currencies, offering a transparent and tamper-resistant framework for a variety of applications. Here’s a brief overview:
Bitcoin:
Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, relies on blockchain technology for its decentralized and secure transactions. Blockchain ensures the integrity of the transaction history, making it resistant to fraud and manipulation.
Ethereum:
Ethereum is a blockchain platform that enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). It expands the use of blockchain beyond simple transactions, allowing for programmable and self-executing contracts.
IBM Food Trust:
IBM Food Trust is a blockchain-based platform designed to enhance transparency and traceability in the food supply chain. It enables stakeholders to track the journey of food products from farm to consumer, reducing the risk of contamination and ensuring food safety.
Walmart and IBM for Supply Chain:
Walmart and IBM collaborated on a blockchain-based solution to improve the transparency and efficiency of the supply chain for food products. The system allows for real-time tracking of products, reducing the time it takes to trace the origin of contaminated food.
3D Printing Technology:
Also referred to as additive manufacturing, 3D printing stands as a transformative technology that facilitates the layer-by-layer creation of three-dimensional objects, revolutionizing various industries, including manufacturing and healthcare.
Stratasys:
As a leading provider of 3D printing solutions, Stratasys offers a diverse range of 3D printers and materials. Widely utilized in aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, their technology excels in rapid prototyping, customized manufacturing, and the production of intricate components.
Ultimaker:
Recognized for its desktop 3D printers, Ultimaker serves professionals, educators, and enthusiasts. These printers find applications in prototyping, design validation, and educational settings, contributing to the accessibility of 3D printing technology.
3D Systems:
A trailblazer in the 3D printing industry, 3D Systems provides a variety of additive manufacturing solutions. Their technologies are instrumental in healthcare for crafting patient-specific medical implants and dental applications, while also playing a crucial role in rapid prototyping and production within aerospace and automotive industries.
Radical Innovation on the Innovation Continuum
The innovation continuum is a concept that illustrates the various stages of innovation, ranging from incremental improvements to radical transformations. It encompasses a spectrum of innovation types, each contributing differently to organizational growth, development, and competitiveness. radical innovation stands out as a transformative force that goes beyond incremental improvements or sustaining advancements. Positioned at the end of the innovation continuum, radical innovation represents a departure from the status quo, introducing groundbreaking changes that redefine industries and create new paradigms. Here are the key stages along the innovation continuum:
- Incremental Innovation:
- Description: Incremental innovation involves making small improvements to existing products, processes, or services. It is often characterized by gradual enhancements and optimizations.
- Example: Regular updates to smartphone models with improved features or performance represent incremental innovation.
- Breakthrough Innovation:
- Description: Breakthrough innovation involves significant advancements or discoveries that may lead to new products, processes, or technologies. It goes beyond incremental improvements and often requires a higher level of risk and investment.
- Example: The development of the first touchscreen smartphone was a breakthrough innovation that changed the way we interact with mobile devices.
- Disruptive Innovation:
- Description: Disruptive innovation introduces entirely new products or services that disrupt existing markets, often challenging established industry leaders. It can create new business models and redefine customer expectations. It typically starts in niche customer segments before expanding and reshaping entire industries. Disruptive innovations challenge the dominance of established players and create new market dynamics.
- Example: The introduction of digital cameras disrupted the traditional film photography industry.
- Open Innovation:
- Description: Open innovation involves collaboration with external partners, including customers, suppliers, and other organizations, to generate ideas, share knowledge, and co-create value. It extends innovation beyond internal boundaries.
- Example: Companies like Procter & Gamble (P&G) engage in open innovation by collaborating with external partners for product development.
- Radical Innovation:
- Description: Radical innovation or transformative innovation represents a complete shift in thinking, often involving the introduction of entirely new technologies, business models, or industries. It has the potential to reshape entire markets.
- Example: The development and widespread adoption of the internet transformed communication, commerce, and various aspects of daily life.
- Sustaining Innovation:
- Description: Sustaining innovation involves continuous improvements to existing products or processes to maintain competitiveness in the market. It aims to sustain the organization’s current market position.
- Example: Regular software updates that enhance the security and functionality of applications represent sustaining innovation.
Understanding the innovation continuum is crucial for organizations seeking to balance short-term gains with long-term competitiveness. Effective innovation strategies often involve a mix of incremental improvements, breakthrough initiatives, and an openness to disruptive or radical innovations to stay adaptable in a dynamic business environment.
What Sets Radical Innovation Apart from Other Types of Innovation
Understanding the nuances that set radical innovation apart from other types is crucial for organizations seeking transformative change. Let’s explore the distinctions by comparing radical innovation with incremental innovation, disruptive innovation, and architectural innovation.
Radical Innovation vs Incremental Innovation
While incremental innovation focuses on making gradual improvements to existing products or processes, radical innovation seeks revolutionary change, often giving rise to entirely new markets. The shift from traditional internal combustion engines to electric vehicles is a prime example of radical innovation, disrupting the automotive industry with groundbreaking technology and sustainable solutions. This transformative leap underscores the dynamic interplay between radical and incremental innovation in shaping industries and propelling technological advancements. The coexistence of these innovation approaches reflects the dual nature of progress—one marked by steady, iterative enhancements and the other by bold, disruptive transformations.
| Aspect | Radical Innovation | Incremental Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of Change | Significant and transformative change. | Gradual improvements to existing elements. |
| Level of Disruption | Can disrupt markets and reshape industries. | Maintains continuity within existing markets. |
| Risk and Investment | Higher risk and investment due to uncertainty. | Lower risk and investment leveraging existing knowledge. |
| Timeline and Pace | Longer timeline for research and adoption. | Quicker implementation with steady progress. |
| Examples | Internet, smartphones, electric cars. | Software updates, and manufacturing improvements. |
| Market Impact | Creates new markets and redefines industries. | Targets existing markets and underserved customer needs. |
| Adaptability and Flexibility | Requires high adaptability and openness to change. | Adaptable at a more manageable pace. |
| Long-Term vs. Short-Term Focus | Long-term focus to establish new directions. | Short-term focus, addressing immediate needs. |
Radical Innovation vs Disruptive Innovation:
Although both are transformative, disruptive innovation aims to replace existing solutions in the market, causing a significant shift. On the other hand, radical innovation introduces entirely new concepts that may coexist or eventually replace current solutions. The advent of digital streaming services, such as Netflix, is a testament to disruptive innovation, reshaping the entertainment industry, while the introduction of smartphones represents radical innovation by creating a new category of devices.
| Aspect | Radical Innovation | Disruptive Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Requires a high level of adaptability to embrace transformative change. | Introduces new products or services that disrupt existing markets, often targeting underserved or overlooked segments. |
| Scope of Change | Broad and transformative, impacting various aspects of an industry or market. | Specifically aimed at disrupting existing markets or industries, challenging established players. |
| Level of Disruption | Can be highly disruptive, especially if it introduces a completely new paradigm. | Intentionally disruptive, aiming to create a shift in market dynamics and hierarchies. |
| Risk and Investment | Involves a higher level of risk and investment due to the uncertainty of introducing something entirely new. | Requires significant risk-taking, but the focus is often on creating a more cost-effective solution for underserved markets. |
| Timeline and Pace | May have a longer timeline for research, development, and market adoption. | Can have a quicker pace of adoption, especially if it offers a simpler, more accessible solution than existing options. |
| Examples | The development of the internet, smartphones, electric cars. | Requires a high level of adaptability to embrace transformative change. |
| Market Impact | Creates new markets and redefines industries, potentially rendering existing technologies obsolete. | Targets existing markets but with the goal of redefining how products or services are delivered. |
| Adaptability and Flexibility | Requires a high level of adaptability to embrace the transformative change. | Requires adaptability but often in response to market shifts caused by disruptive innovations. |
| Long-Term vs. Short-Term Focus | Often has a long-term focus, establishing new directions for industries. | May have both short-term and long-term effects, but the initial focus is on market disruption. |
Radical innovation can be broad and transformative, affecting multiple aspects of an industry. Disruptive innovation, on the other hand, specifically targets the disruption of existing markets by introducing alternative solutions. Both types of innovation, however, play crucial roles in shaping the evolution of industries and markets.
Radical Innovation vs Architectural Innovation:
Architectural innovation involves changing the overall structure of a system, while radical innovation introduces entirely new systems or paradigms. In strategic management, radical innovation goes beyond incremental changes, bringing about radically innovative change that transforms the core aspects of how a business operates. For instance, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into business processes represents radical innovation in strategic management, revolutionizing decision-making and analytics.
| Aspect | Radical Innovation | Architectural Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Involves the introduction of entirely new technologies, business models, or approaches, leading to transformative change. | Development of the internet, smartphones, and electric cars. |
| Scope of Change | Broad and transformative, impacting various aspects of an industry or market. | Targets specific components or structures within existing products or systems to enhance performance, efficiency, or functionality. |
| Level of Disruption | Can be highly disruptive, challenging established norms, and potentially rendering existing technologies or business models obsolete. | Disruption is significant but often limited to specific components or elements, with less potential to reshape entire industries. |
| Risk and Investment | Involves a higher level of risk and investment due to the uncertainty of introducing something entirely new. | May involve moderate risk, often focused on improving existing components or structures rather than creating something entirely novel. |
| Timeline and Pace | May have a longer timeline for research, development, and market adoption due to the complexity of introducing something entirely new. | Can have a quicker pace of adoption, especially if the changes are focused on specific components rather than a complete overhaul. |
| Examples | Development of the internet, smartphones, electric cars. | Upgrading the internal components of a product, redesigning the architecture of a software system. |
| Market Impact | Creates new markets and redefines industries, potentially reshaping how products or services are perceived and utilized. | Impacts specific aspects of a market, often leading to enhanced performance or functionality without necessarily altering the market landscape. |
| Adaptability and Flexibility | Requires a high level of adaptability to embrace transformative change. | Requires adaptability but often within the context of improving existing structures and components. |
| Long-Term vs. Short-Term Focus | Often has a long-term focus, establishing new directions for industries. | Can have both short-term and long-term effects, but the initial focus is on improving specific aspects of existing products or processes. |
Advantages of Radical Innovation and Disadvantages
Radical innovation, characterized by groundbreaking changes and transformative shifts in products, services, or processes, offers several advantages for organizations striving to stay at the forefront of their industries and it comes with its fair share of challenges. The high level of risk associated with venturing into uncharted territories can pose a significant disadvantage, as the outcome of introducing entirely new concepts or technologies remains uncertain.
Advantages of Radical Innovation:
1. Creates Sustainable Competitive Advantages:
- Radical innovation allows organizations to pioneer new products, services, or business models that set them apart from competitors. These innovations create a unique value proposition, fostering long-term competitiveness that is challenging for others to replicate. cultivating an innovation culture within the organization becomes pivotal in sustaining this advantage over time.
- Example: The introduction of the iPhone by Apple brought about a revolution in the smartphone industry, establishing a sustainable competitive advantage. The seamless integration of hardware and software, complemented by a user-friendly interface, set a benchmark that competitors found challenging to match.
The Value Proposition Canvas is a strategic tool that plays a crucial role in the process of radical innovation, helping organizations create sustainable competitive advantages. Developed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur, the canvas is part of the broader Business Model Canvas framework and focuses specifically on understanding customer needs and crafting compelling value propositions.
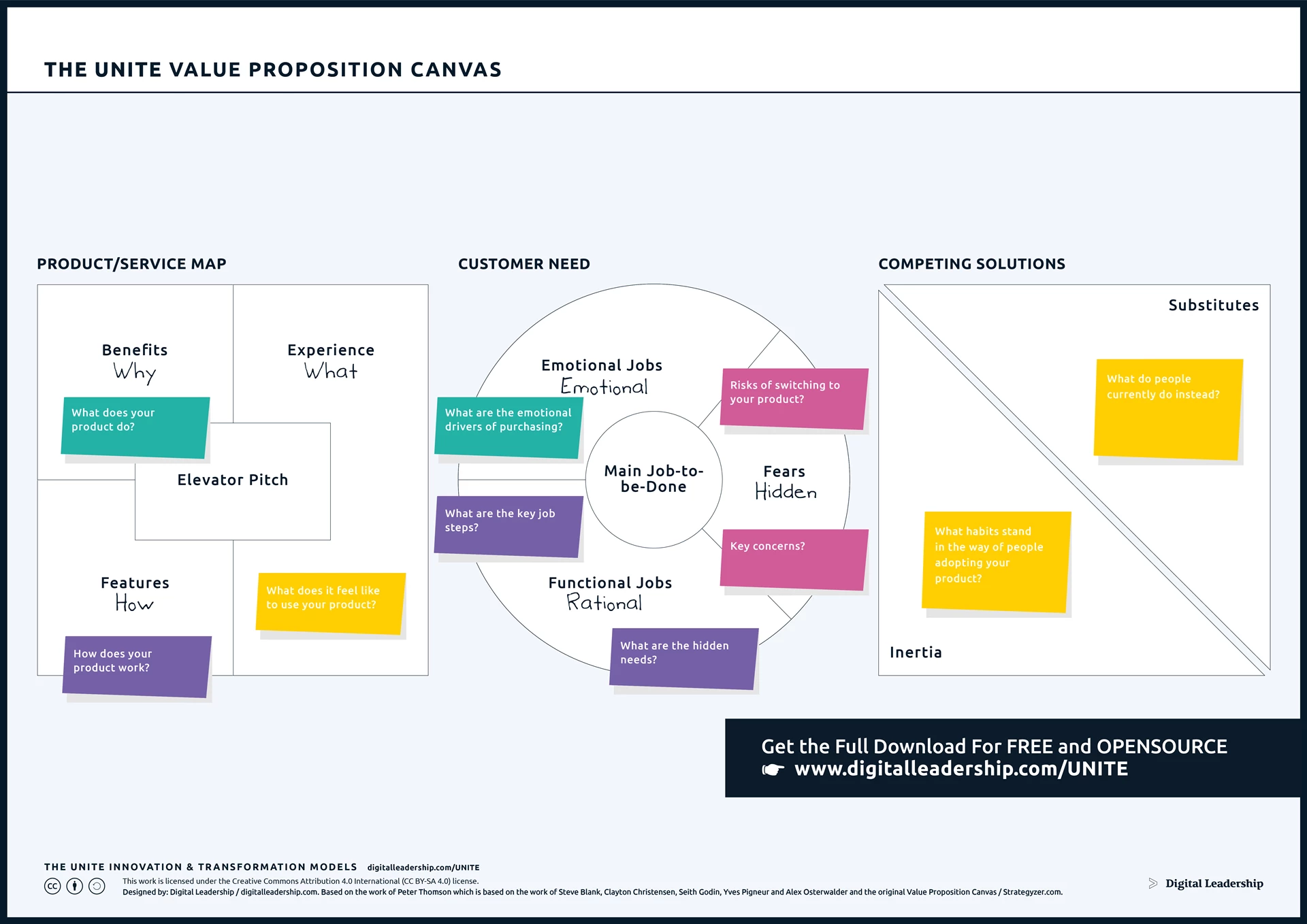
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Based on the work of Peter Thomson which is based on the work of Steve Blank, Clayton Christensen, Seith Godin, Yves Pigneur and Alex Osterwalder and the original Value Proposition Canvas
2. Opens New Markets and Revenue Streams:
- Unveiling groundbreaking solutions enables organizations to explore untapped markets and revenue streams by engaging with new customer segments. This expansion creates fresh opportunities for revenue generation, adding diversity to the organization’s income streams. Fostering an innovation culture becomes instrumental in identifying and capitalizing on these new market possibilities.
- Example: Tesla’s foray into the electric vehicle market represented a radical innovation that unlocked new markets. By crafting high-performance electric cars with broad appeal, Tesla not only reshaped the automotive industry but also emerged as a leader in sustainable transportation.
3- Positions Organizations as Industry Leaders:
- Organizations pioneering radical innovation are acknowledged as industry leaders and trendsetters. This not only draws in customers but also amplifies the organization’s influence within the industry, charting the course for future advancements.
- Example: Google’s relentless innovation in search algorithms, online services, and artificial intelligence has solidified its status as an industry leader in technology. The company’s trailblazing efforts in areas like machine learning and cloud computing have established the gold standard for the tech industry.
Disadvantages of Radical Innovation:
1- Involves Higher Risk and Uncertainty:
- Pursuing radical innovation is inherently riskier than incremental changes. The uncharted territory of groundbreaking ideas introduces uncertainties, and the outcome may not always align with initial expectations, leading to potential setbacks.
- Example: The development of entirely new pharmaceutical drugs involves high risk and uncertainty. Clinical trials may not always yield the desired results, leading to significant investments without guaranteed success.
2. Requires Substantial Investments:
- The development and implementation of radical innovations often demand substantial financial investments. Research, development, testing, and the scale-up of new concepts can strain organizational budgets, particularly if the returns are not immediate.
- Example: The development of SpaceX’s reusable rocket technology, exemplified by the Falcon 9, required substantial investments in research, development, and testing. The success of this radical innovation, however, has positioned SpaceX as a leader in space exploration.
3. May Face Resistance from Established Players:
- Established players within an industry may resist radical innovations, especially if these changes threaten existing business models or market positions. Resistance can come from competitors, industry associations, or regulatory bodies, adding complexity to the adoption process.
- Example: The introduction of streaming services faced initial resistance from traditional cable and broadcast networks. Platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video disrupted established models, leading to industry-wide transformations.
Radical Innovation Characteristics
Radical innovation is characterized by its:
Disruptive Impact:
Radical innovations wield a transformative influence on industries and markets, causing a disruptive upheaval. They boldly challenge the established norms, displacing existing players, and fundamentally reshaping entire sectors. A prime illustration of this is the introduction of the iPhone by Apple. By consolidating multiple functions—phone conversations, internet surfing, and music playback—into a singular device, it not only revolutionized user experience but also dethroned established mobile phone manufacturers, sparking a profound change in the mobile phone industry.
Paradigm Shift:
The aftermath of radical innovations often manifests as a paradigm shift, fundamentally altering established practices. A compelling case study is the ascent of e-commerce sites such as Amazon, which boldly contested traditional retail methods. This shift redirected the focus from physical storefronts to online purchasing, concurrently transforming customer behaviour. The cumulative effect was a substantial reshaping of the entire retail sector.
Novelty and Breakthrough:
Radical innovations are distinguished by their introduction of novel and groundbreaking concepts, products, or services that transcend incremental improvements. An exemplary instance is the emergence of blockchain technology catalyzed by Bitcoin. This innovation disrupted traditional financial systems by presenting a decentralized and transparent approach to transactions, ushering in new possibilities for secure and efficient peer-to-peer interactions.
Radical Innovation Process Steps
1. Identify Opportunities for Radical Change:
The first step in the radical innovation process involves actively identifying areas within the organization or the industry where radical change can bring about transformative outcomes. This may involve assessing market trends, technological advancements, or customer needs that present opportunities for revolutionary solutions.
2. Encourage a Culture of Experimentation and Risk-Taking:
Fostering a culture that encourages experimentation and risk-taking is crucial for radical innovation. This involves creating an environment where employees feel empowered to explore unconventional ideas, take calculated risks, and challenge the status quo. Embracing failure as a valuable learning experience is integral to this culture.
3. Collaborate with External Partners for Diverse Perspectives:
Collaboration with external partners, whether they are other organizations, research institutions, or startups, brings diverse perspectives to the innovation process. External collaborators can provide fresh insights, access to complementary expertise, and contribute to a broader innovation ecosystem that enhances the likelihood of radical breakthroughs.
4. Prototype and Test Innovative Ideas Rapidly:
Rapid prototyping is a key step in the radical innovation process. It involves creating tangible models or representations of innovative ideas quickly to test their feasibility and gather feedback. This iterative testing allows for the refinement and improvement of concepts before full-scale implementation, reducing the risk of costly mistakes.
5. Learn from Failures and Iterate on Concepts:
Embracing failure as an inherent part of the innovation process is critical for organizations pursuing radical change. Learning from failures provides valuable insights that can inform subsequent iterations of ideas. Continuous iteration based on customer feedback and lessons learned ensures that the innovation process remains dynamic and responsive to evolving challenges.
The 3 Horizons of Innovation
Radical innovation can be summarized as a combination of new, revolutionary technology and new ways of conducting business. The 3 horizons of the innovation framework emphasize innovation, change, and growth on all levels. It is important to mention that an organization is only able to achieve long-term growth if it works concurrently on all three horizons to improve the business model on all levels.

Designed By: Digital Leadership AG – Inspired by the work of Baghai, Coley, and White
but how can you ensure stable output at scale and still be innovative? Innovation vs. standardization is a balancing act, that most organizations fail to understand. With the UNITE Horizons of Growth framework, you know exactly when and how to improve, transform or innovate your business.
Horizon 1: Improve an Existing Business
The first horizon is the most basic step and refers to the status quo of your business. It represents what your business is currently doing, including products, services, and your existing market.
In this phase, you mainly apply incremental innovation and publish new versions of your product or service. Further, you make use of and optimize already existing technology. This stage aims to continuously improve your products and services to serve your current market.
Horizon 2: Transfer an Existing Business
Horizon 2 goes one step further. It aims at innovating your business models to better serve your current and new markets. The goal is to reach out to a larger audience and establish new distribution channels. Besides new markets, you should also offer extra products and services to your existing customers.
By introducing new, innovative models, you will also have the opportunity to rethink your vision for the future, ability, industry, technology, and long-term business goals. This lays out the fundamentals for future growth and innovation.
Horizon 3: Innovate a New Business Model – Disruptive & Radical Innovation
While the first two horizons are more or less of an incremental nature, horizon 3 is where actual change happens that can have a long-lasting effect on your company. Therefore, the focus of Horizon 3 is all about radical innovation.
This step should be combined with Horizon 2. While Horizon 2 delivers new business models and extends your current customer base, horizon 3 incorporates technological innovations to bring your new vision to life. In this context, radical innovation focuses on new technologies to conduct business to achieve better market positions in the long term.
Horizons 1, 2, and 3 do not only differ in terms of results but also in the time and effort it takes to plan and implement them. While horizon 1 can relatively easily be implemented, horizon 3 may take years to fully reap the desired results.
Conclusion
Radical innovation, fueled by digital business models is a powerful driver of transformative change, reshaping industries and propelling societies into new territories. By deeply understanding customer needs and iteratively refining solutions, organizations can create sustainable competitive advantages. This customer-centric approach not only addresses current market demands but also uncovers latent opportunities, positioning innovators as industry leaders. Understanding its meaning, examples, and characteristics equips organizations to navigate the dynamic landscape of innovation successfully.
Frequently asked questions:
1- How do organizations approach risk-taking in the context of radical innovation, and what is the level of tolerance for failure in these initiatives?
Organizations embracing radical innovation acknowledge the inherent risk, fostering a culture that tolerates failure as a stepping stone to success.
2- Is Apple a radical innovation?
Yes, Apple is often regarded as a company that has consistently demonstrated radical innovation. From the introduction of the Macintosh computer in 1984, which revolutionized personal computing with its graphical user interface, to the iPod, iPhone, iPad, and more recent products like the Apple Watch, the company has continually pushed boundaries. The company’s emphasis on design, user experience, and cutting-edge technology has positioned it as a pioneer in the tech industry, making Apple synonymous with radical innovation.
3- What is a radical transformation?
A radical transformation involves a complete and fundamental change, often disrupting existing norms and creating new paradigms.
Related Posts
The Four Types of Innovation and Their Impact on Business Success
In business landscape, innovation isn't just a buzzword; it's a strategic imperative1
View Full article50 Innovation Examples: Exciting Innovative Ideas in Business
In the Business environment, strategic innovation has taken centre stage as a1
View Full articleInnovation Strategy: Developing Innovative Strategies in Business
Innovation has become an imperative for organizations worldwide, yet the multitude of1
View Full article“Innovation Coaching” An Inside Look at The Catalyst for Organization Change
Huston, we have a problem In today's business, the drive towards innovation1
View Full article






























 Book How to Create Innovation
Book How to Create Innovation